Changing the Password Secure your account by updating your password in just a few steps. Log in, navigate to...
Blog categories
- GNSS antennas (17) click
- GNSS receivers (14) click
- ELTEHS products (16) click
- GNSS Product Selection (10)
- Press releases (2) click
- ELT RTK Base (13) click
Search in blog
Latest posts
-
 13. Local Net. Password. ShutdownRead more
13. Local Net. Password. ShutdownRead more -
 12. Mounting2025-05-074 views 0 LikedRead more
12. Mounting2025-05-074 views 0 LikedRead moreThe device should be installed in a cool, dry, and dust-free environment, avoiding direct sunlight and exposure to...
-
 11. LED indicators2025-05-073 views 0 LikedRead more
11. LED indicators2025-05-073 views 0 LikedRead moreThis section explains the LED indicators on advanced (wired) and budget (wireless) base stations. The purple LED...
-
 10. Wi-Fi Setup Using WPS PBC2025-05-074 views 0 LikedRead more
10. Wi-Fi Setup Using WPS PBC2025-05-074 views 0 LikedRead moreThis section covers Wi-Fi setup using WPS PBC for the ELT_RTKBase base station. Starting from version 1.7.8, the...
-
 9. Connection2025-05-073 views 0 LikedRead more
9. Connection2025-05-073 views 0 LikedRead moreThis section covers essential safety precautions during hardware setup, including antenna installation, SD card...
Popular posts
-
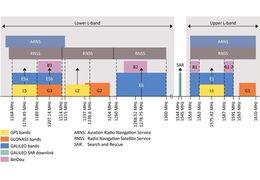 L1, L2, L5, L3, and simply L frequency bands:2023-04-0975705 views 15 LikedWhy there are so many GNSS bands and names?Read more
L1, L2, L5, L3, and simply L frequency bands:2023-04-0975705 views 15 LikedWhy there are so many GNSS bands and names?Read more -
 Connectors: BNC, TNC, SMA, MCX, MMCX, IPEX/U.FL — what's this alphabet soup?2023-04-0912502 views 16 LikedWhat connector is the best?Read more
Connectors: BNC, TNC, SMA, MCX, MMCX, IPEX/U.FL — what's this alphabet soup?2023-04-0912502 views 16 LikedWhat connector is the best?Read more -
-
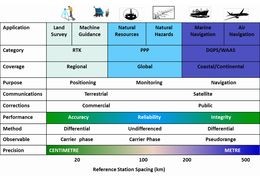
 Unicore UPrecise application2023-09-148874 views 35 LikedHow to use the UPrecise application from Unicore?Read more
Unicore UPrecise application2023-09-148874 views 35 LikedHow to use the UPrecise application from Unicore?Read more -
Featured posts
-
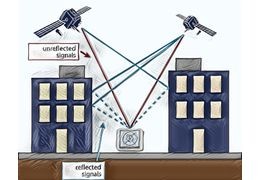 Groundplane and multipath2023-03-294090 views 13 LikedHow to deal with GNSS signal reflections.Read more
Groundplane and multipath2023-03-294090 views 13 LikedHow to deal with GNSS signal reflections.Read more -
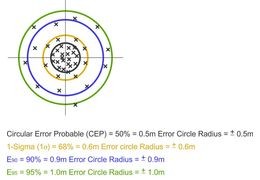
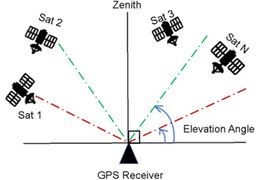 Elevation angle and errors2023-04-095910 views 9 LikedWhy satellite elevation angle is important?Read more
Elevation angle and errors2023-04-095910 views 9 LikedWhy satellite elevation angle is important?Read more -
 Big antennas, Small antennas, caseless antennas2023-04-092688 views 8 LikedWhy antennas have so different sizes?Read more
Big antennas, Small antennas, caseless antennas2023-04-092688 views 8 LikedWhy antennas have so different sizes?Read more -

-
 Lightning protection that doesn't exist2023-04-092615 views 12 LikedHow to escape from the lightning ?Read more
Lightning protection that doesn't exist2023-04-092615 views 12 LikedHow to escape from the lightning ?Read more


Latest comments